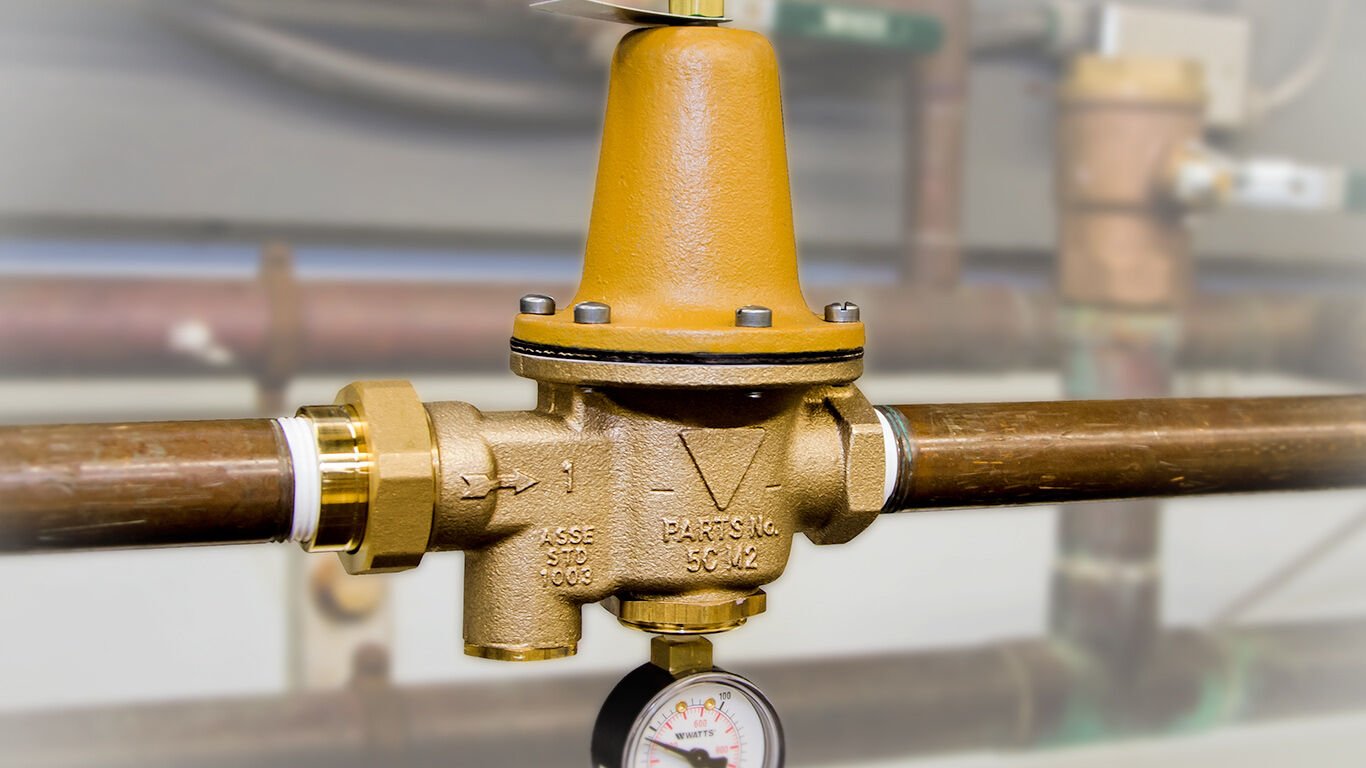
Pressure regulator valves come in various shapes and sizes. Each type is made for certain tasks and working conditions.
Most regulators fit into two groups:
Selecting the appropriate type is very important. Each design handles pressure changes differently. This makes some better for certain tasks than others.
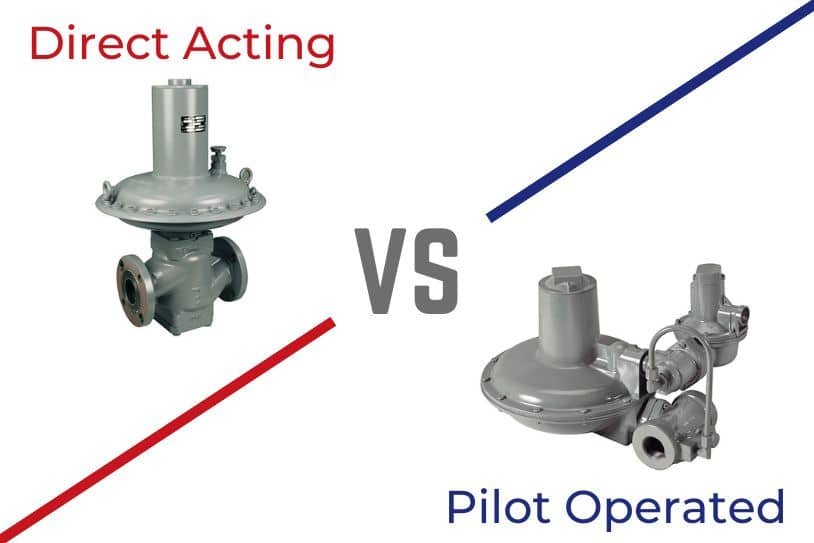
Direct-Acting vs. Pilot-Operated
Direct-acting regulators use a spring. It pushes on a diaphragm that opens and closes the valve when needed. They are usually more intuitive, easy to fix, and respond quickly to pressure changes. They are mostly good for uses that need lower to medium flows. High accuracy isn’t required for these applications.
Pilot-operated models have a pilot valve. This valve helps control the main valve. This arrangement provides increased control. It works well for high-flow or high-pressure tasks. You often find it with gas cylinders or storage tanks.
Pilot-operated types keep set pressure stable during flow changes. Direct-acting types are cheaper and easier to install.
Spring-loaded and dome-loaded
Spring-loaded and dome-loaded regulators rely on different mechanisms to establish the outlet pressure. Spring-loaded regulators use a simple spring mechanism. They work well with most water or gas pipes.
Dome-loaded regulators use a gas-filled dome instead of a spring. This design reacts faster to changes in flow or pressure. The dome-loaded type works best for tasks needing quick, smooth, and sensitive movement. This includes lab and process facilities.
In addition, they perform excellently in applications where clean, repeatable control is a priority.
Specialized Application Designs
Not all regulators are created equal. Specialized application designs exist for specific needs. Gas and steam regulators have seals or diaphragms. These parts help handle thermal or chemical damage.
Dual-stage regulators lower pressure in two steps. This is helpful when the inlet pressure changes. To choose the right one, think about the application type, the medium, and the pressure range.
Choosing Your Ideal Regulator
Picking the right pressure regulator valve is key to making your system run well. First, get a clean picture of what exactly your system is supposed to do. Pay attention to the fluid you’re using and the practical application of your environment.
Aligning specifications with these unknowns helps your system run smoothly and extends its life.
Understanding System Demands
Determine where your system’s lowest and highest pressure points are located. Understand your process's inlet and outlet flow rates. These numbers help you determine the right regulator.
A plumbing system that runs at 10 bar needs a regulator to keep the pressure steady at that level. If the flow changes a lot, you want a regulator that handles big changes and maintains control.
Matching regulator specs, such as flow curves and control ranges, to your application helps prevent sudden drops or spikes while in use.
Fluid Type and Material Match
Fluid Type and Material Match What travels through your pipes affects your match with the regulator. Whether it is water, oil, air, or other specialty chemicals, each has unique reactions to metals or plastics. Brass is an excellent choice for drinking water applications.
If you are dealing with corrosive fluids, you want to use stainless steel or specialty polymers for rust and wear resistance. If you make the wrong match, the regulator will likely have a short lifespan.
Look for third-party certifications, such as ISO or UL, as a good indicator of quality.

Balancing performance and cost
The ideal match strikes a compromise between cost and performance. Higher-quality models, like dome-loaded regulators, cost more. But, they manage pressure swings better and last longer.
Don’t forget about maintenance costs, either—less expensive regulators often must more repairs. Find a solution that meets all your requirements without breaking the bank.
Critical Sizing Considerations
Critical Sizing Considerations: Too big, and you can’t provide enough pressure. Too small, and you can’t stay in the driver’s seat. Find your ideal pipe size with maker flowcharts and get what you need.
Using certified sizing methods can prevent dangerous and expensive errors.